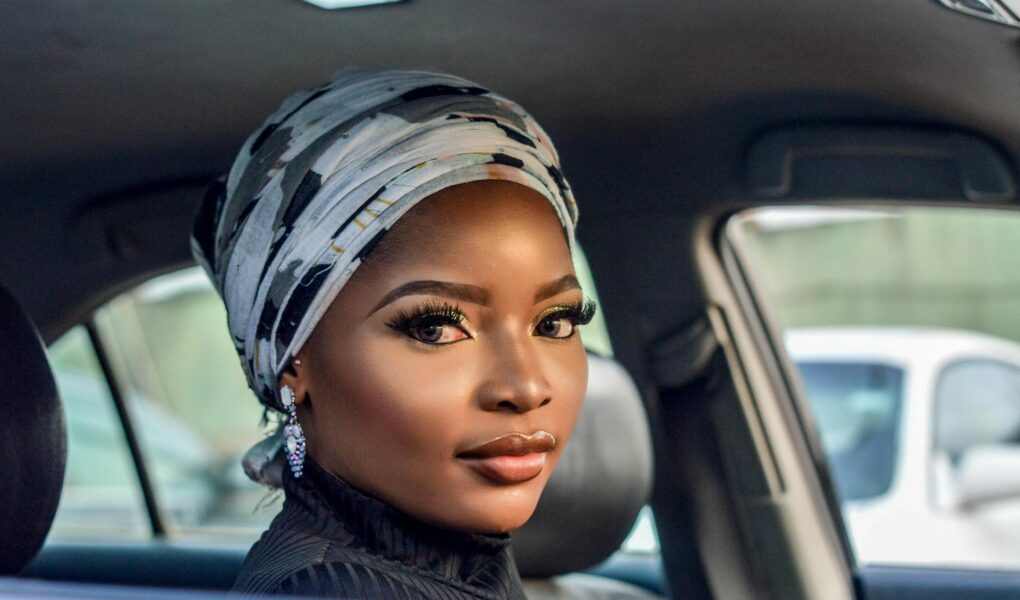
African skin tones are incredibly diverse and beautiful, ranging from rich brown to dark chocolate hues, light to dark shades of brown, copper to dark brown complexions, and light to medium brown with olive undertones. The beauty of African skin tones lies in their uniqueness and the stories they tell about the people who possess them. It is important to discuss African skin tones because they are often underrepresented in mainstream media and beauty standards, leading to a lack of representation and appreciation for the diversity within the African continent.
Key Takeaways
- African skin tones are diverse and beautiful, with a wide range of shades and hues.
- Melanin is the pigment that determines skin color, and there are two types: eumelanin and pheomelanin.
- West African skin tones range from rich brown to dark chocolate hues, while East African skin tones vary from light to dark shades of brown.
- Southern African skin tones include copper to dark brown complexions, while North African skin tones are light to medium brown with olive undertones.
- Central African skin tones are dark brown to black, and African skin tones have cultural significance in terms of beauty standards and identity.
The Science of Skin Pigmentation: Understanding Melanin and its Types
Melanin is the pigment responsible for determining the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. It is produced by cells called melanocytes, which are located in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are two main types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is responsible for darker skin tones, while pheomelanin is responsible for lighter skin tones.
The amount and type of melanin produced by an individual’s melanocytes determine their skin color. People with more eumelanin have darker skin tones, while those with more pheomelanin have lighter skin tones. The production of melanin is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, exposure to sunlight, and hormonal changes.
African Skin Tones by Region: A Brief Overview
Africa is a vast continent with diverse cultures and ethnicities, resulting in a wide range of skin tones. The continent can be divided into several regions, each with its own unique characteristics. These regions include West Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, North Africa, and Central Africa.
West African Skin Tones: Rich Brown to Dark Chocolate Hues
West Africa is known for its rich brown to dark chocolate skin tones. This region is home to diverse ethnic groups, including the Yoruba, Igbo, and Akan people. Famous individuals with West African skin tones include Lupita Nyong’o, Idris Elba, and Naomi Campbell.
East African Skin Tones: Light to Dark Shades of Brown
East Africa is characterized by light to dark shades of brown skin tones. This region is home to ethnic groups such as the Maasai, Kikuyu, and Somali people. Famous individuals with East African skin tones include Barack Obama, Lupita Nyong’o, and Liya Kebede.
Southern African Skin Tones: Copper to Dark Brown Complexions

Southern Africa is known for its copper to dark brown complexions. This region is home to ethnic groups such as the Zulu, Xhosa, and Ndebele people. Famous individuals with Southern African skin tones include Nelson Mandela, Trevor Noah, and Charlize Theron.
North African Skin Tones: Light to Medium Brown with Olive Undertones
North Africa is characterized by light to medium brown skin tones with olive undertones. This region is home to ethnic groups such as the Berber, Arab, and Tuareg people. Famous individuals with North African skin tones include Rami Malek, Amr Waked, and Yasmine Bleeth.
Central African Skin Tones: Dark Brown to Black Complexions
Central Africa is known for its dark brown to black complexions. This region is home to ethnic groups such as the Bantu, Pygmy, and Fang people. Famous individuals with Central African skin tones include Samuel Eto’o, Alek Wek, and Patrice Lumumba.
The Cultural Significance of African Skin Tones: From Beauty Standards to Identity
African skin tones hold great cultural significance within African societies. They are often associated with beauty standards and play a crucial role in shaping individual and collective identities. In many African cultures, lighter skin tones are often considered more desirable and associated with beauty, wealth, and social status. This has led to the perpetuation of colorism, a form of discrimination based on skin color, within African communities.
Celebrating African Skin Tones: Embracing Diversity and Challenging Colorism
It is important to celebrate the diversity of African skin tones and challenge colorism within African communities. By embracing and appreciating the beauty of all skin tones, we can promote inclusivity and equality. This can be done through education, representation in media and beauty industries, and challenging societal norms that perpetuate colorism.
In conclusion, African skin tones are incredibly diverse and beautiful. Understanding the science behind skin pigmentation and appreciating the different skin tones found across Africa can help promote inclusivity and challenge colorism. By celebrating the beauty of all African skin tones, we can create a more inclusive and equal society. It is time to embrace diversity and challenge societal norms that perpetuate discrimination based on skin color.